CannaKeys 360° Terpene Search is your source for the expanding endocannabinoid research on terpenes. Terpenes are a key component in the Entourage Effect or collective effect a patient experiences when using cannabis as a result of the many constituents present.
Search by terpene and get a summary of the science with a filterable dashboard and comprehensive list of primary and related studies.
Beta-Caryophllene
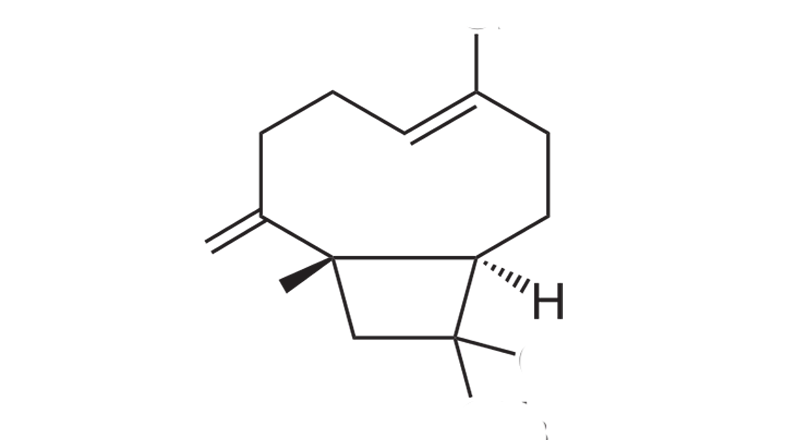
Beta-caryophyllene is a sesquiterpene that binds with CB2, TRPV1, and PPAR-γ receptor sites. Depending on the concentration, its scent is spicy and peppery, with a solid warm, woody aroma and an undertone of citrus. Beta-caryophyllene is commonly the predominant terpene in cannabis, especially after decarboxylation. ß-caryophyllene may be gastroprotective, analgesic, anticarcinogenic, antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, anti-epileptic and neuroprotective.
Bisabolol
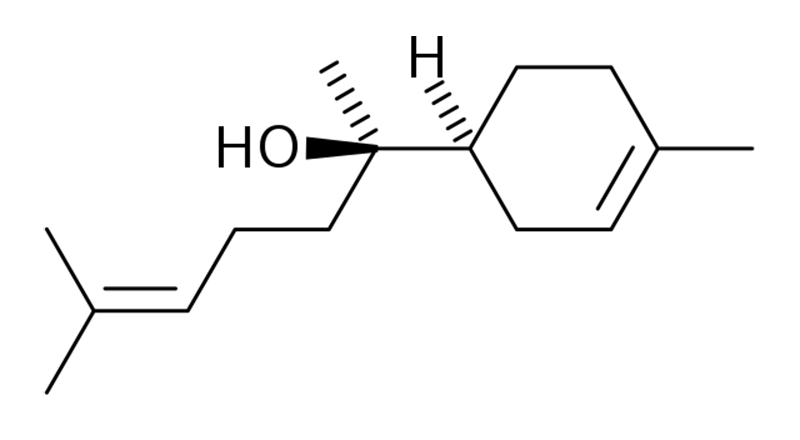
Bisabolol is a sesquiterpene occurring in significant amounts in several plant species, such as Psidium guajava (guava), Matricaria chamomilla (German chamomile), and cannabis. Bisabolol may have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidant, cardio-protective, antimicrobial, anti-parasitical, gastro-protective, and nephroprotective effects.
Borneol
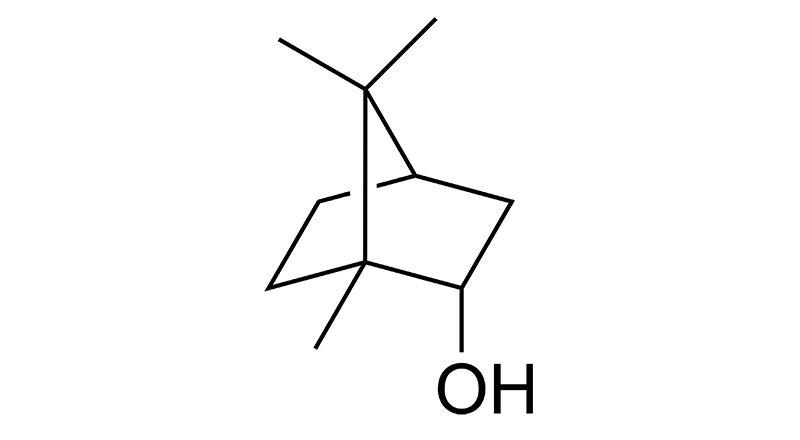
Borneol is a minor terpene in cannabis. It has a woody, herbal scent and is also found in Turmeric, thyme, rosemary and ginger. Borneol may have anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, antibacterial, and analgesic effects.
Camphene
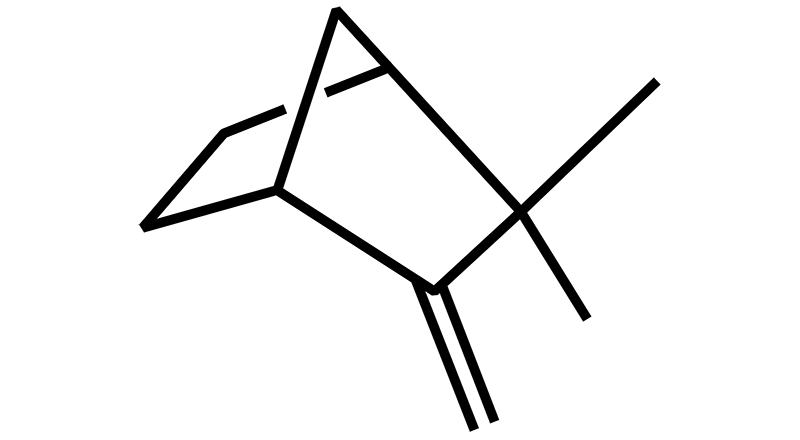
Camphene is a monoterpene found in cannabis as well as ginger, camphor, rosemary and citronella. It has woodsy, fir-needle smell with a light camphor scent. Camphene medicinal properties include anti-microbial, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Eucalyptol
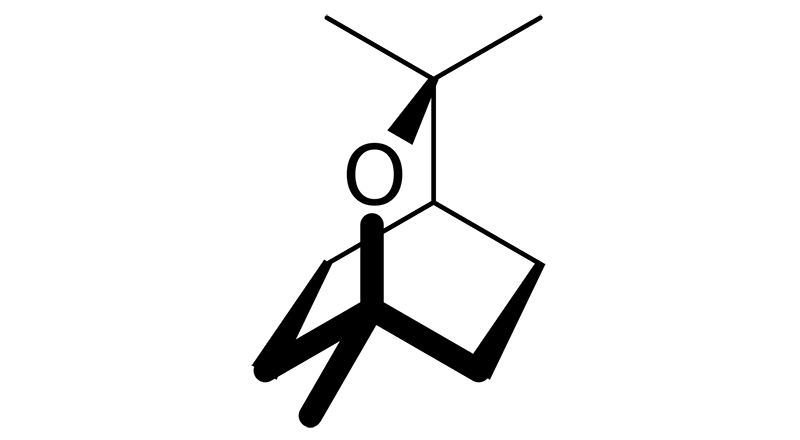
Eucalyptol, also know as Cineole, is found in cannabis as well as the eucalyptus tree. It has a minty, cooling earthy scent. Eucalyptol has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anxiolytic, cough suppressant, broncholytic, mucolytic, choleretic, antiseptic, anticancer, and antimicrobial.
Geraniol
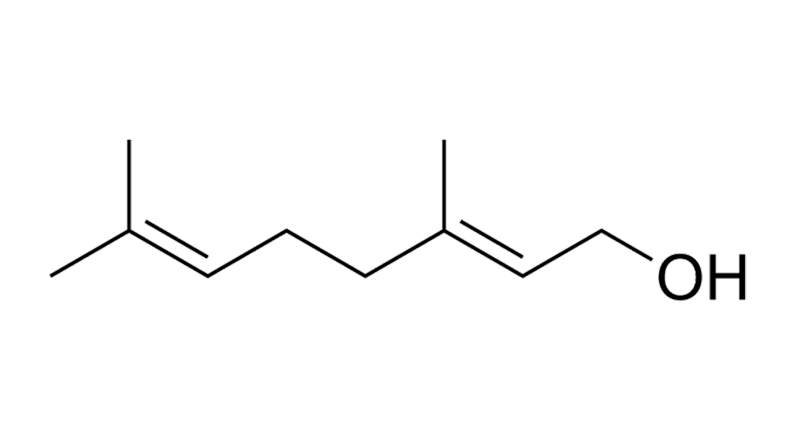
Geraniol is a monoterpenoid with a rose-reminiscent scent. It is found naturally in cannabis, geraniums, rose oil, and lemons. Geraniol has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Preclinical evidence shows it may have neuroprotective, anxiolytic and antidiabetic effects.
Humulene
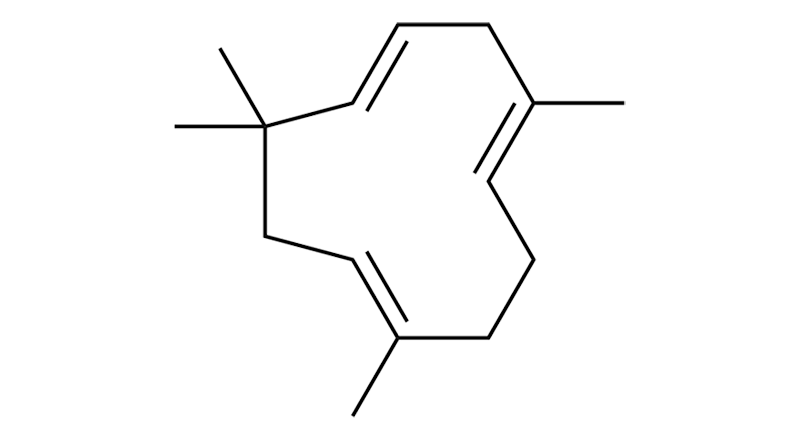
Humulene is a sesquiterpene that, while relatively common, is often found in low concentrations. As its name suggests, it provides an earthy, humus-like aroma. Humulene has properties that are anti-inflammatory, anti-asthmatic, antibacterial, analgesic, and have some anticancer activity.
Limonene
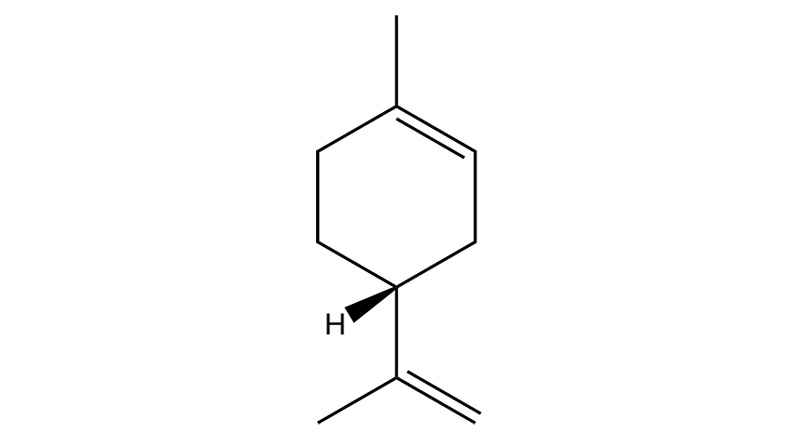
Limonene is a relatively stable monoterpene and the second most abundant terpene in nature after pinene. Upon inhalation, limonene becomes rapidly bioavailable in humans.
Linalool
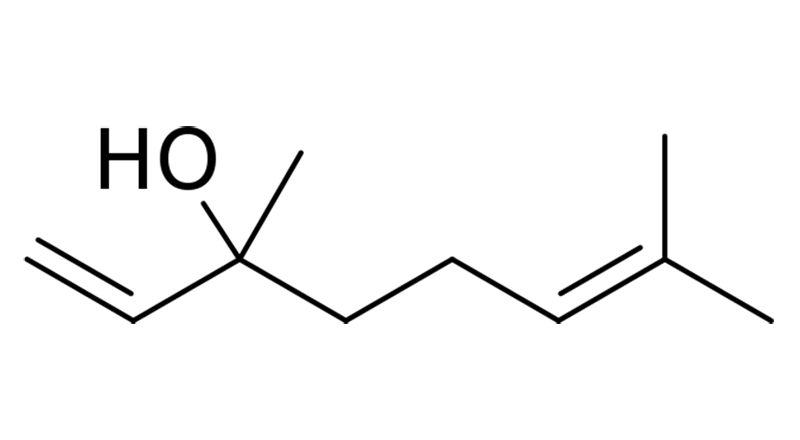
Linalool is a monoterpene that offers a floral, lavender-like scent with a hint of spiciness. It displays a great variety of potential health effects because it can act on many receptors and biochemical pathways. Studies have found Linalool has anxiolytic, neuroprotective, antidepressant, anti-stress, antihypertensive, analgesic and anticonvulsant properties.
Myrcene
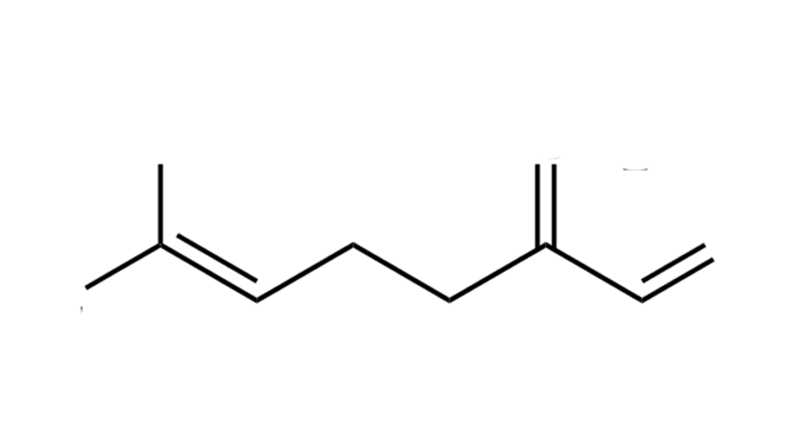
Myrcene is a monoterpene that, in diluted forms, tastes like mango. Myrcene makes THC more biologically available by increasing the saturation level and speed at CB1 and thus boosting THC’s properties. Higher concentrations of β-myrcene in cannabis tend to produce feelings of heavy, deep relaxation. Other potential properties of Myrcene include analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, and sleep inducing effects.
Nerolidol
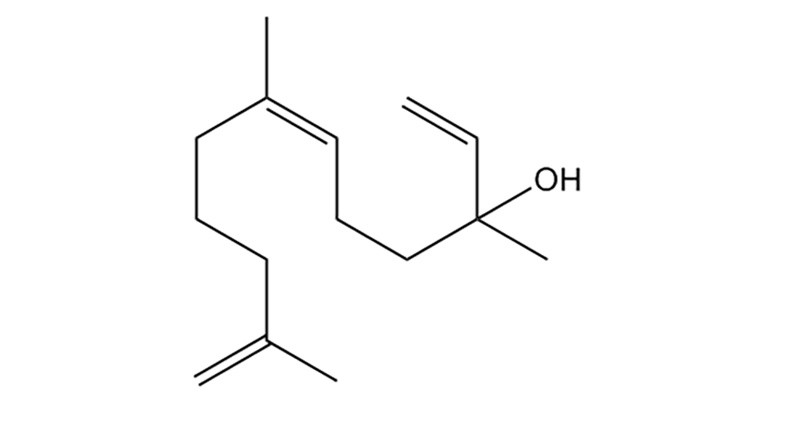
Nerolidol is a sesquiterpene with a fresh, woody scent. Natural sources include cannabis, tea tree oil, and citrus peel. Nerolidol can enhance skin penetration to improve the bioavailability of drugs using transdermal and topical applications. Preclinical evidence shows Nerolidol has sedative, anxiolytic, antispasmodic, antifungal and anti-parasitic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Ocimene
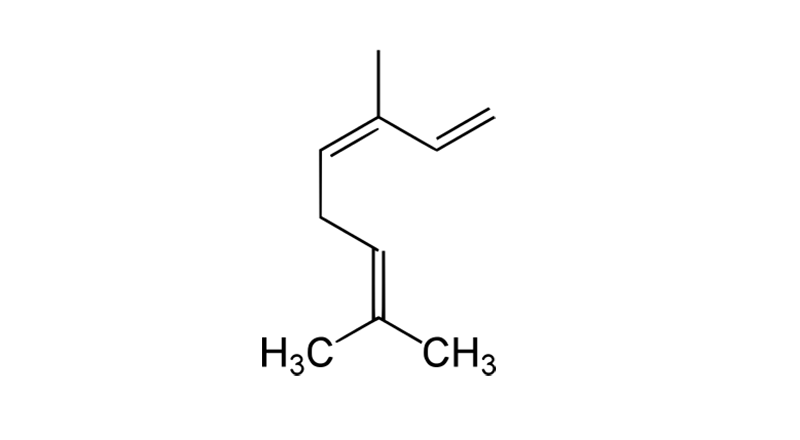
Ocimene is a monoterpene with a perfume-like floral scent. It is used as a flavoring agent and additive. Natural sources include cannabis, tarragon, basil, mint and parsley. Ocimene is thought to possess anticonvulsant, antifungal, antibacterial, antitumor and antihypertensive properties.
Phytol
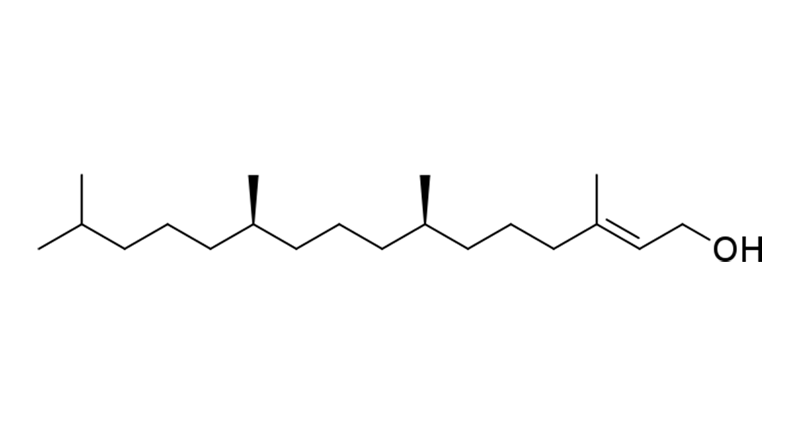
Phytol is a diterpene richly represented in nature as part of the larger molecule chlorophyll, which gives leaves their green color and is essential in photosynthesis. Natural sources include cannabis and green tea. Phytol may have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-convulsant, antimicrobial, anti-parasitic, anxiolytic, sedating and anti-obesity effects.
Pinene
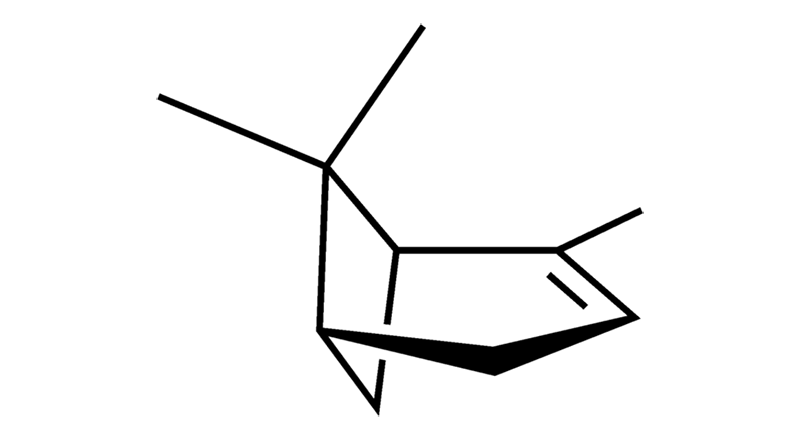
Pinene is a monoterpene that is the most commonly encountered terpene in nature with a pine-like woody scent. Natural sources include rosemary, conifers (pine, cedar, redwood, etc.) coriander, thyme and cannabis. Pinene exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial, analgesic, and bronchodilating activity.
Sabinene
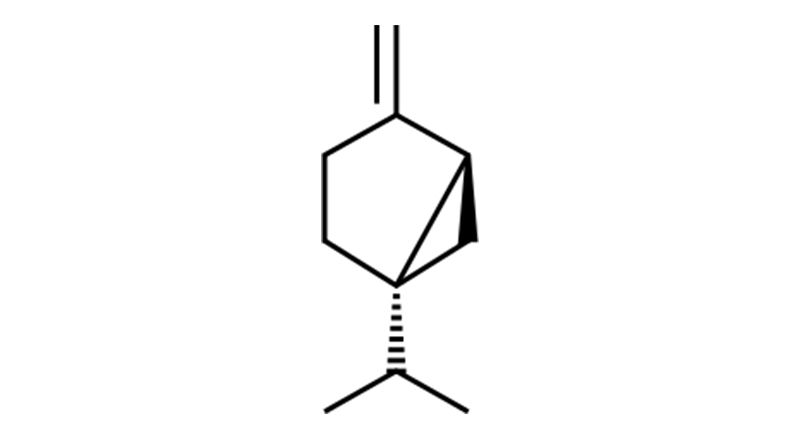
Sabinene is a bicyclic monoterpene isolated from the essential oils of various plant species. Natural sources include wild carrot seeds. Sabinene exhibits anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-microbial, antidiabetic, analgesic, and antioxidant effects.
Terpineol
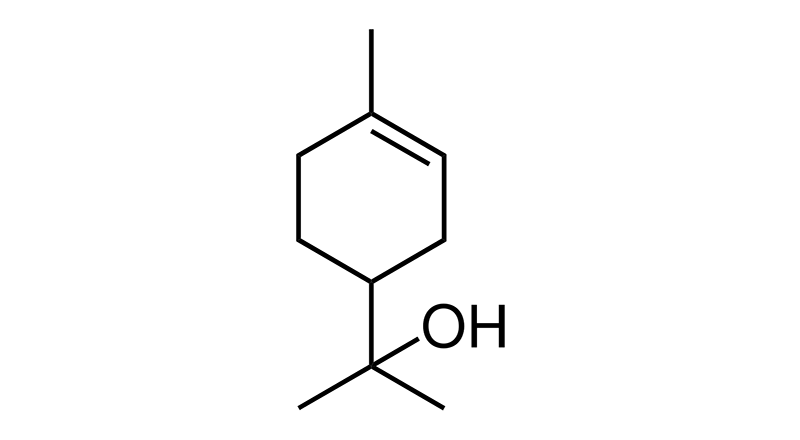
Terpineol is a monoterpene with a piney lilac scent. Natural sources include cannabis, pine trees, tea tree oil, limes. Alpha-terpineol enhances the skin’s permeability to lipid soluble compounds and may improve topical applications of cannabinoid products. Terpineol may have antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties.
Terpinolene
Terpinolene is a monoterpene with a complex aroma profile similar to lilac. It is present in low concentrations in cannabis, citrus fruits, lilac and tea tree oil. Terpinolene may have sedating, anxiolytic, anti-cancer, antibacterial, antioxidant properties.
There are at least 120 confirmed and characterized cannabis-based terpenes, with some sources claiming upwards of 200 have been discovered. We include cannabis-based terpenes once they have proven therapeutic effects discovered in clinical trials.
Additional factors to keep in mind:
- A terpene concentration of at least 0.05% is necessary to expect pharmacological effects in humans.
- Studies using isolated terpenes may show different results than with whole plant based terpenes.
- Methods of combining terpenes and other cannabis constituents can be used to produce synergistic effects (ensemble effect).
- Testing labs don’t take enantiomers (spatial arrangements of the terpene molecule) into account when analyzing terpenes. While both have the same molecular formula due to the difference in shape they can produce significantly different results. For example, α-pinene is not β-pinene, the same goes for limonene enantiomers , linalool enantiomers, and other terpene enantiomers.
- Terpenes, and monoterpenes in particular, oxidize and degrade quickly when in contact with air making terpene concentrations in cannabis unreliable measurements within days.
As trends in cannabinoid and terpenoid research indicate new clinical approaches are warranted, we can help support your clinical practice and keep you up to date with the best resources and scientific data available.
Not a CannaKeys Subscriber?
Check out our terpene dashboard demo for ß-Caryophyllene

