To understand cannabinoids, you must know how they work in the endocannabinoid system. The classical endocannabinoid system (ECS) consists of endocannabinoids, their corresponding receptor sites, metabolizing enzymes, and endocannabinoid tone. Beyond these classical components, you’ll find the relatively new idea of the endocannabinoidome (eCBome), which describes the larger environment interacting with the ECS. The interaction between the ECS and eCBome is not a one-way street but a complex cross-talk-based mechanism that we can harness to improve patient outcomes.
To help you discern their differences and why they matter in the clinical setting, follow the links below to foundational information organized by cannabinoid types, cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoid tone, and the endocannabinoidome.
Phytocannabinoids
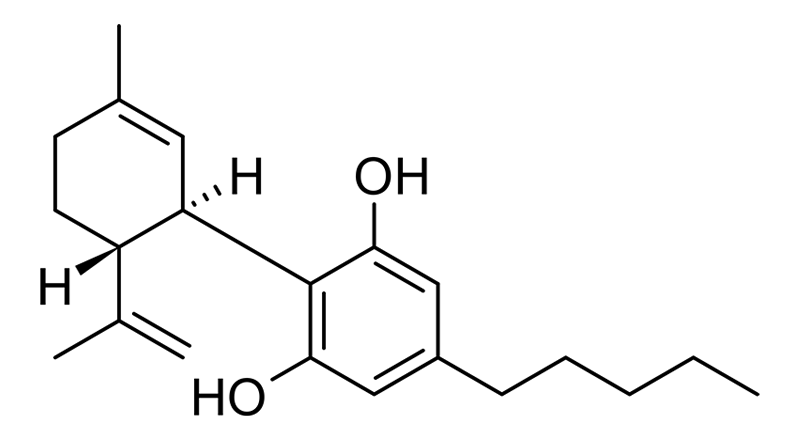
Phytocannabinoids are cannabinoids produced by plants. Over 150 individual cannabinoids have been found in cannabis; we include phytocannabinoids once research indicates they may induce a specific therapeutic effect on a patient population.
Endocannabinoids
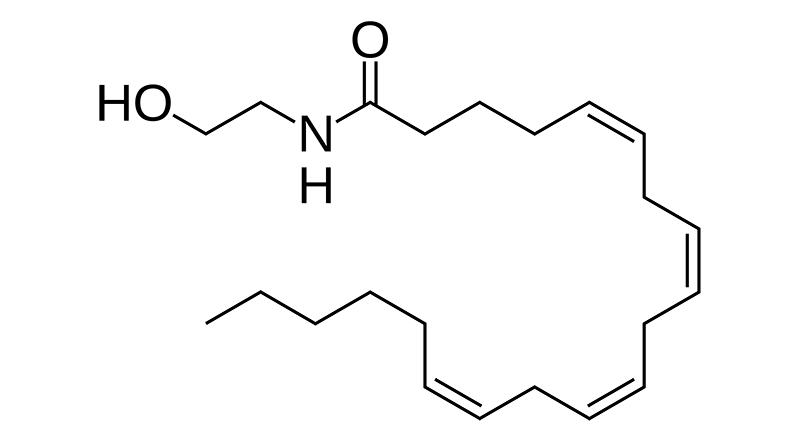
Endocannabinoids are cannabinoids made by the human body. We include endocannabinoids, endocannabinoid analogs, and their primary metabolizing enzymes once research indicates that they have potential clinical relevance.
Synthetic cannabinoids
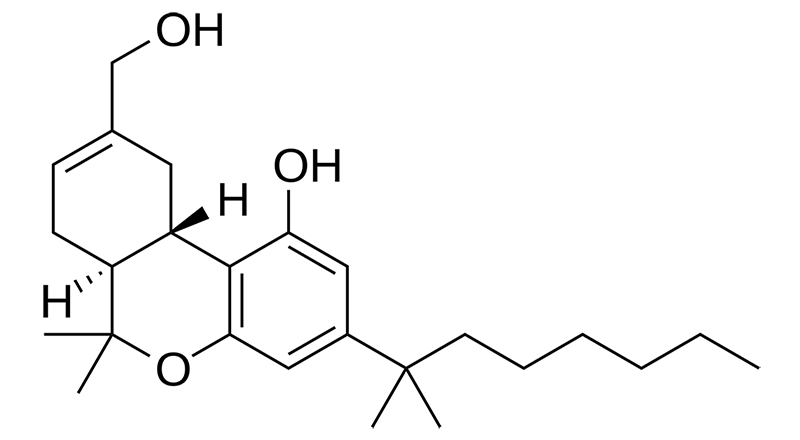
Synthetic cannabinoids are manufactured but used primarily for research rather than patient populations. Synthetic cannabinoids are included once research indicates they have potential relevance in the clinical setting.
Pharmaceutical cannabinoids
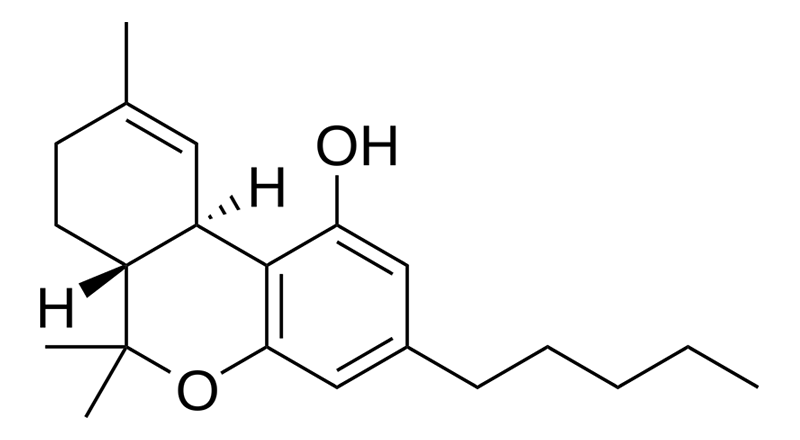
Pharmaceutical cannabinoids are cannabinoid-based drugs that are readily available by prescription. We organize pharmaceutical cannabinoid research data by the ratio of THC to CBD or the cannabis chemotype to which they correspond.
Endocannabinoidome
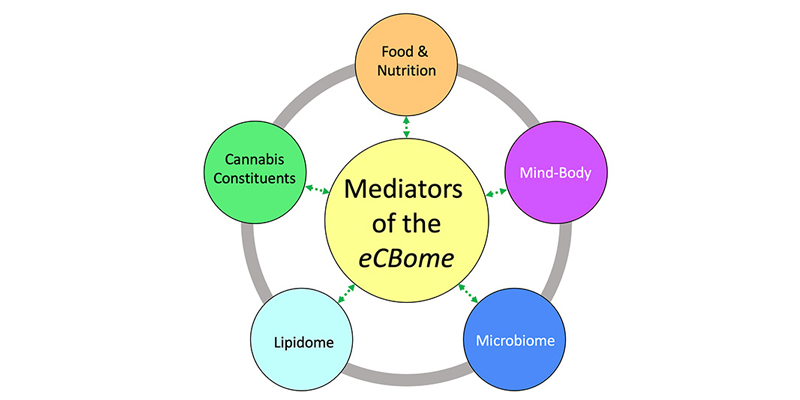
The endocannabinoidome includes cannabis constituents, food, nutraceuticals, mind-body approaches, the microbiome, the lipidome and certain psychotropics that interact with, or modulate, the endocannabinoid system.
Endocannabinoid receptor sites
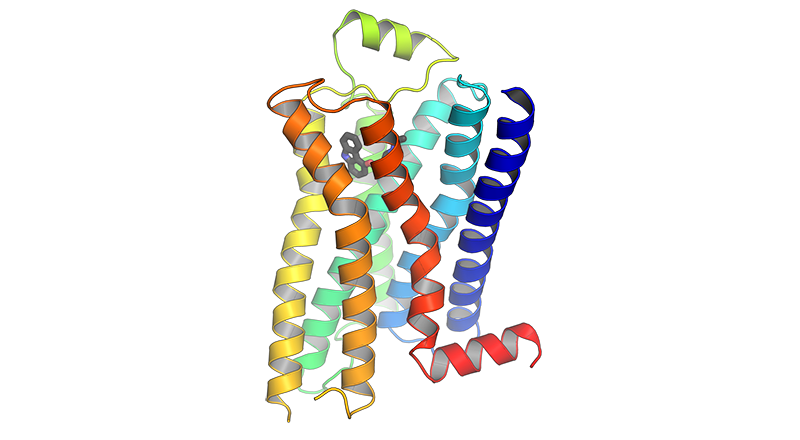
Endocannabinoid receptor site resource pages include CB1, CB2, GPR55 with a deeper dive into the expected effect associated with agonism or antagonism at that receptor and a list of agonists or antagonists with their receptor binding affinities.
Endocannabinoid tone
Endocannabinoid tone and the medical conditions associated with deficient and excessive tone as well as practical steps to enhance or reduce e-tone.
As trends in cannabinoid research indicate that new clinical approaches are warranted, we can help support your clinical practice and keep you up-to-date with the best resources and scientific data available.
Not a CannaKeys Subscriber?
Check out our cannabinoid dashboard demo for THCV

